
Mastering Git: A Beginner’s Guide to Essential Commands and Workflow
Table of Contents
Version control is an essential skill for developers, and Git is the most widely used tool for managing code changes. Whether you're working on a solo project or collaborating with a team, Git helps you track changes, revert to previous versions, and collaborate seamlessly. If you're new to Git, this beginner-friendly guide will walk you through the most important Git commands and how to use them effectively.
What is Git?
Git is a distributed version control system that allows you to track changes in your codebase. It helps you:
- Save different versions of your project.
- Collaborate with others without overwriting work.
- Revert to previous versions if something goes wrong.
It’s a must-learn tool for anyone working in software development, data science, or even content creation.
Getting Started with Git
1. Install Git
Before diving into Git, you need to install it on your system. Here’s how:
- Windows: Download the installer from git-scm.com.
- Mac: Use Homebrew:
brew install git. - Linux: Use your package manager, e.g.,
sudo apt install git.
2. Configure Git
Once installed, set up your Git username and email. This information will be attached to your commits.
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email "your.email@example.com"
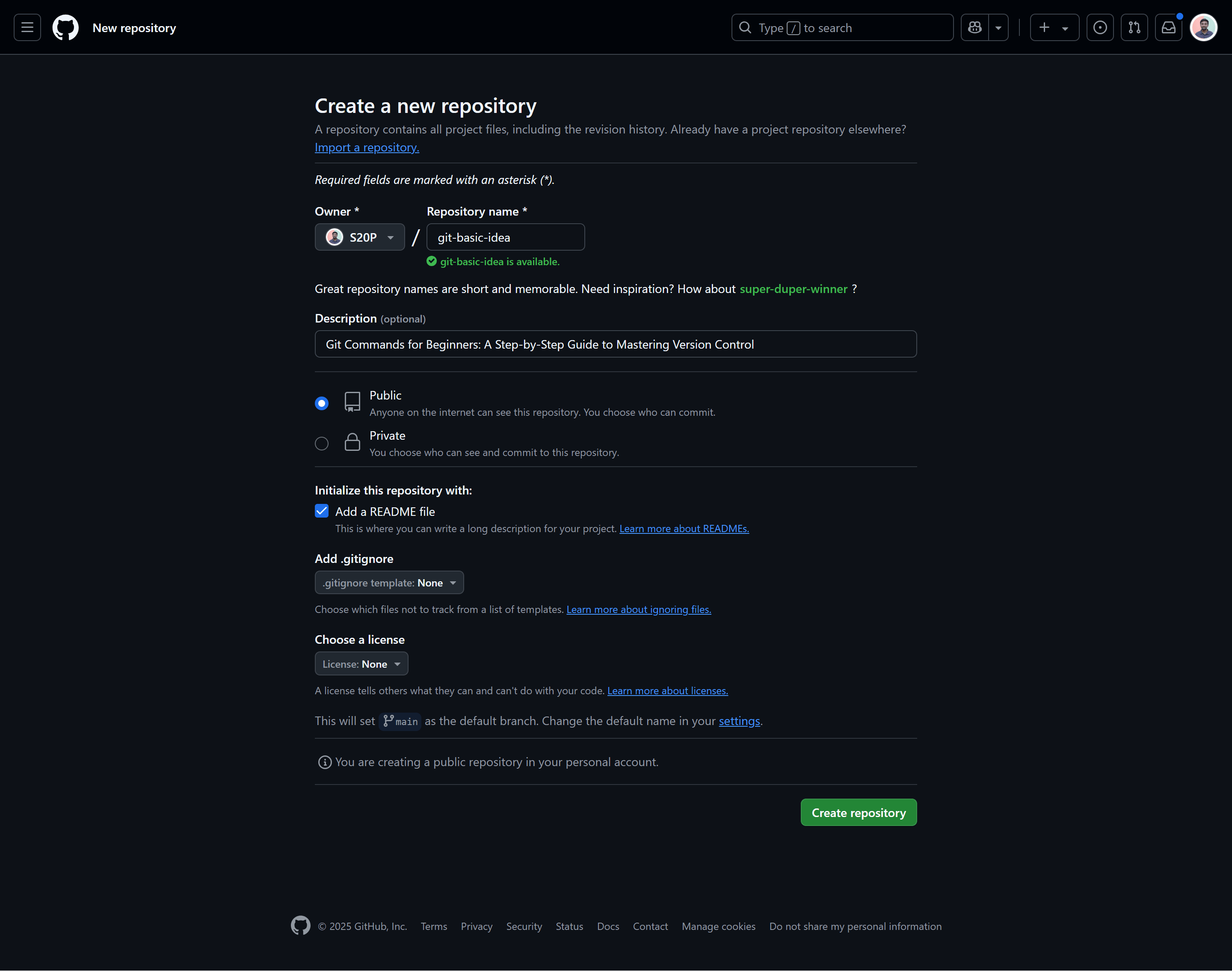
3. Creating a New Repository on GitHub
GitHub is a popular platform for hosting Git repositories. Here’s how to create one:
Log in to your GitHub account.
Click the "New Repository" button.
Add a repository name, description, and optionally initialize it with a README file.
Click "Create Repository."
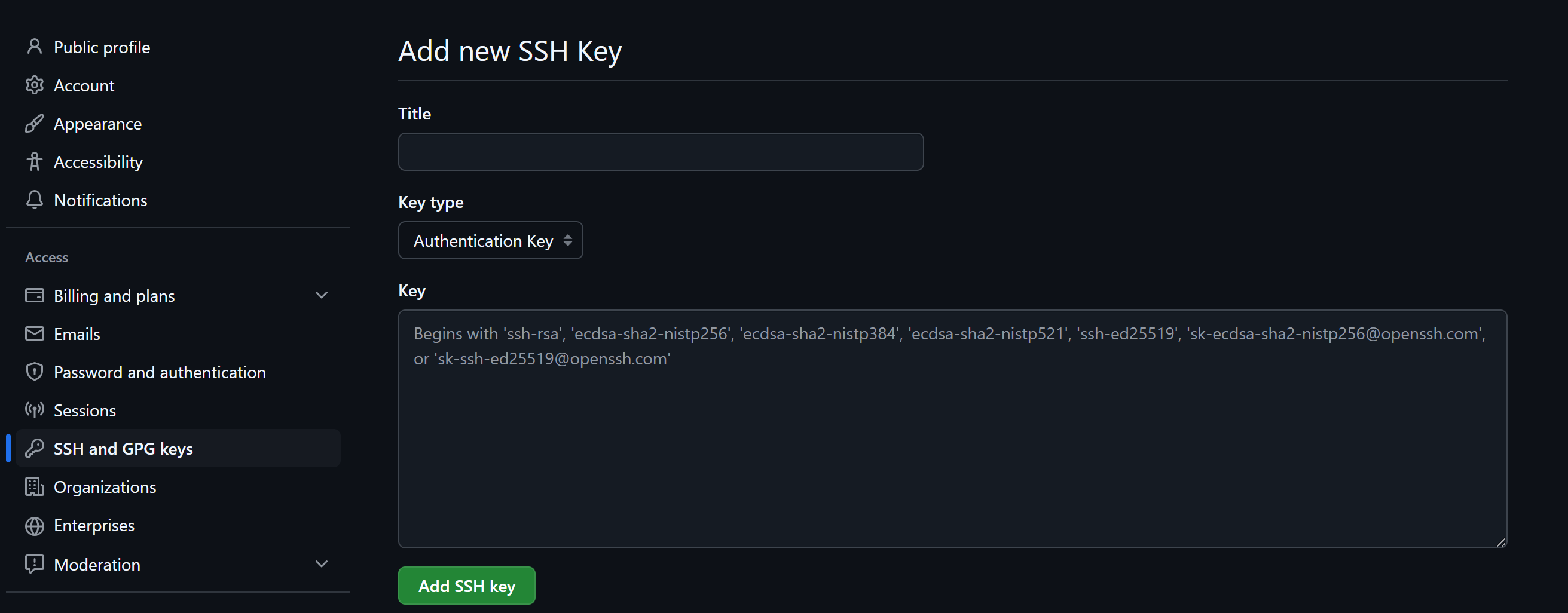
4. Add an SSH Key to GitHub
Using SSH keys allows you to securely connect to GitHub without entering your credentials every time.
- Generate an SSH key:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"Replace "your_email@example.com" with your GitHub email address.
- Copy the generated key and add it to GitHub > Settings > SSH and GPG keys.
- Click New SSH Key, add a title, paste the key, and save.
Essential Git Commands for Beginners
1. Initialize a Git Repository
To start using Git in your project, navigate to your project folder and run:
git init
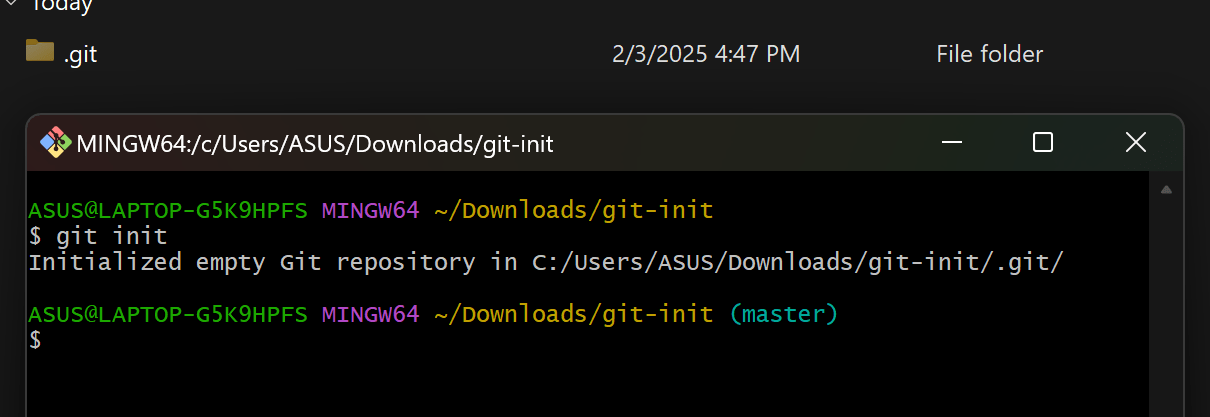
This creates a hidden .git folder to track changes.
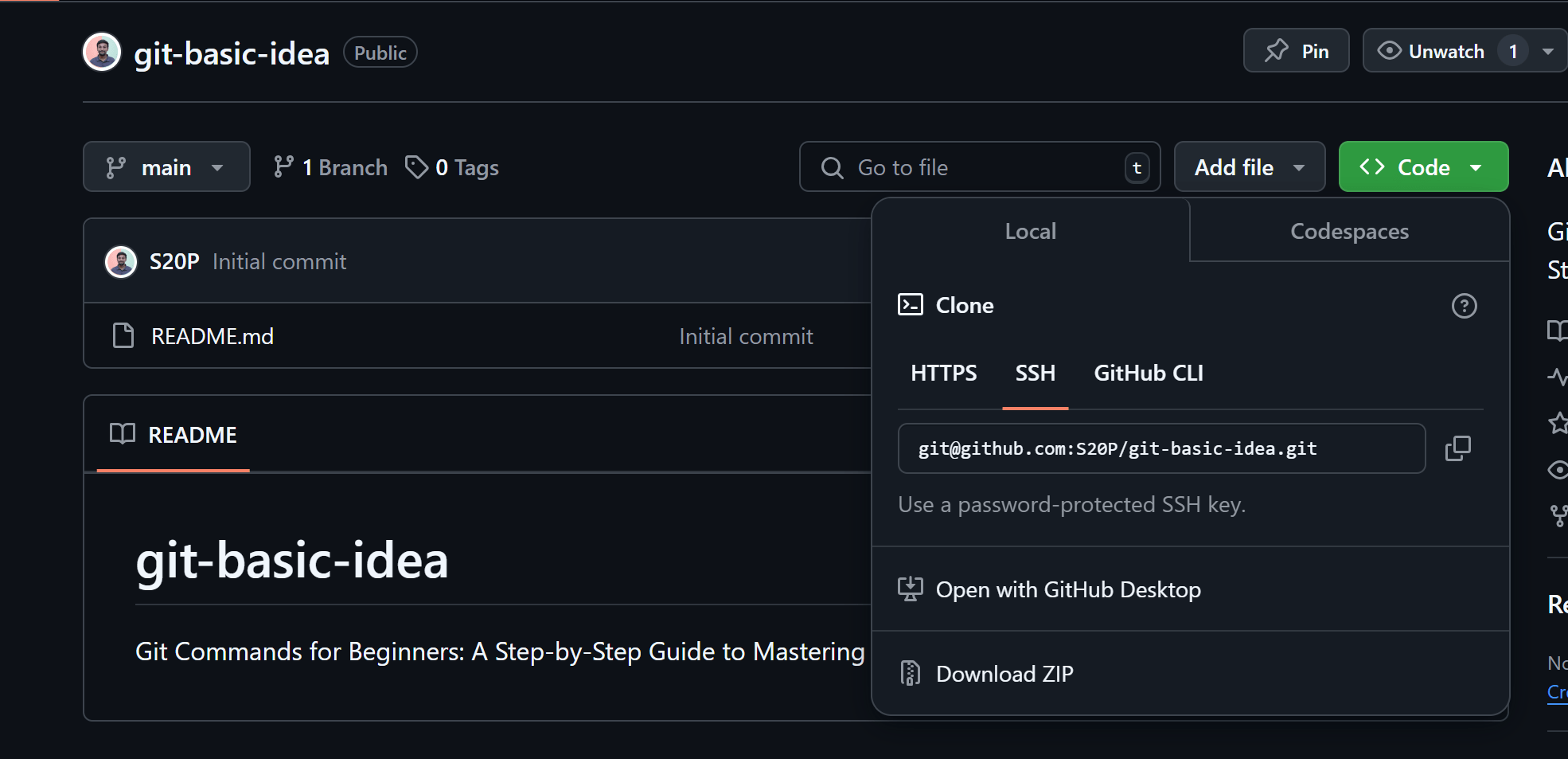
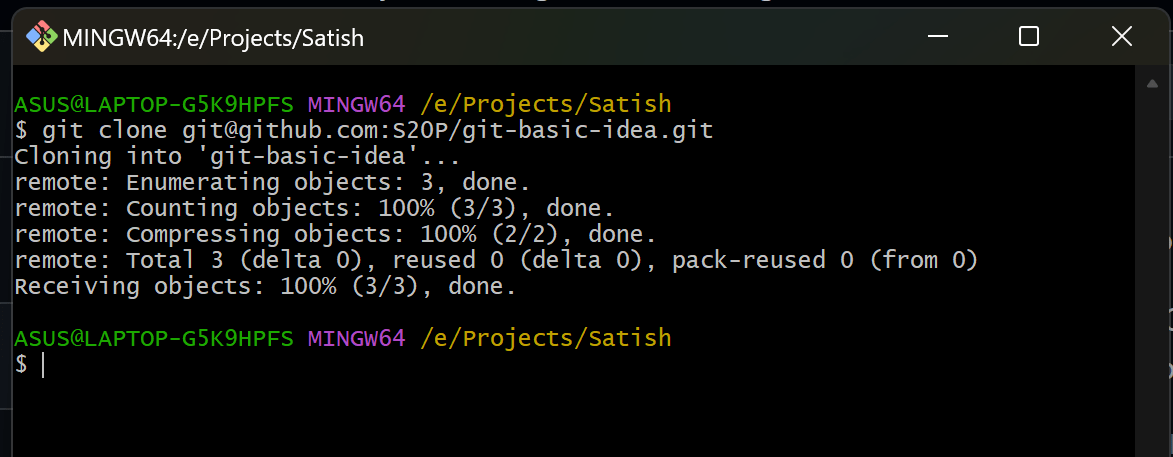
2. Clone a Remote Repository
To work on an existing project, clone it from a remote repository like GitHub:
git clone <repository-url>
3. Add Files to the Staging Area
Prepare files for committing:
git add <file-name>
To add all files in the directory:
git add .
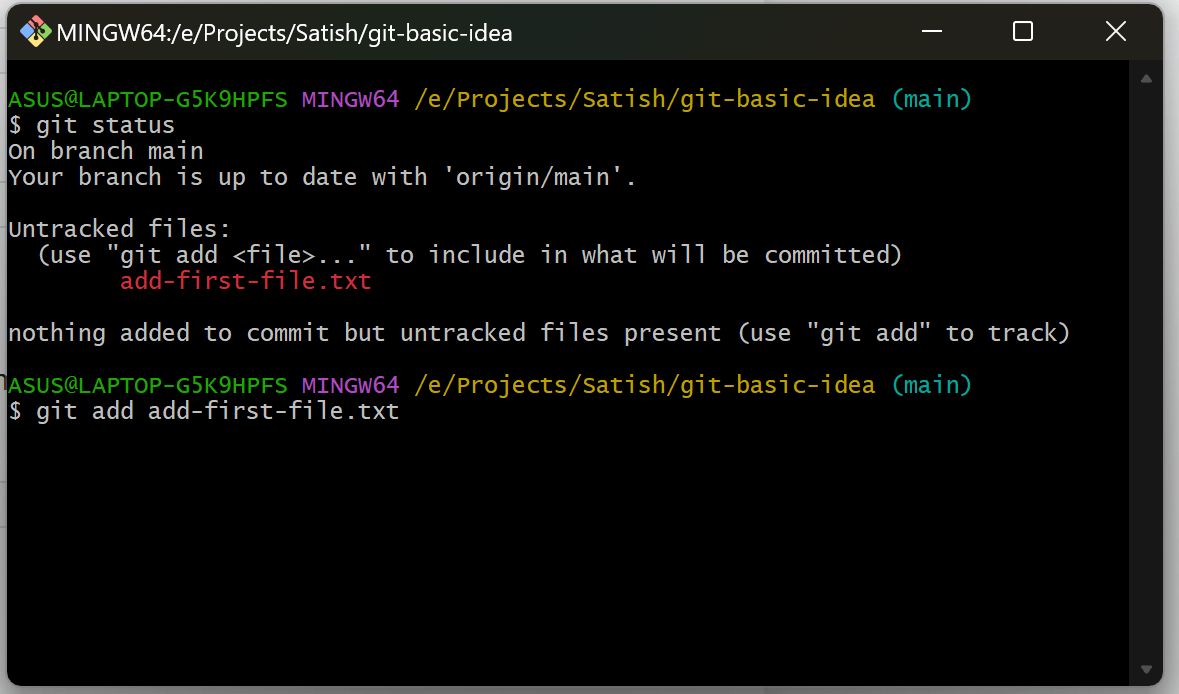
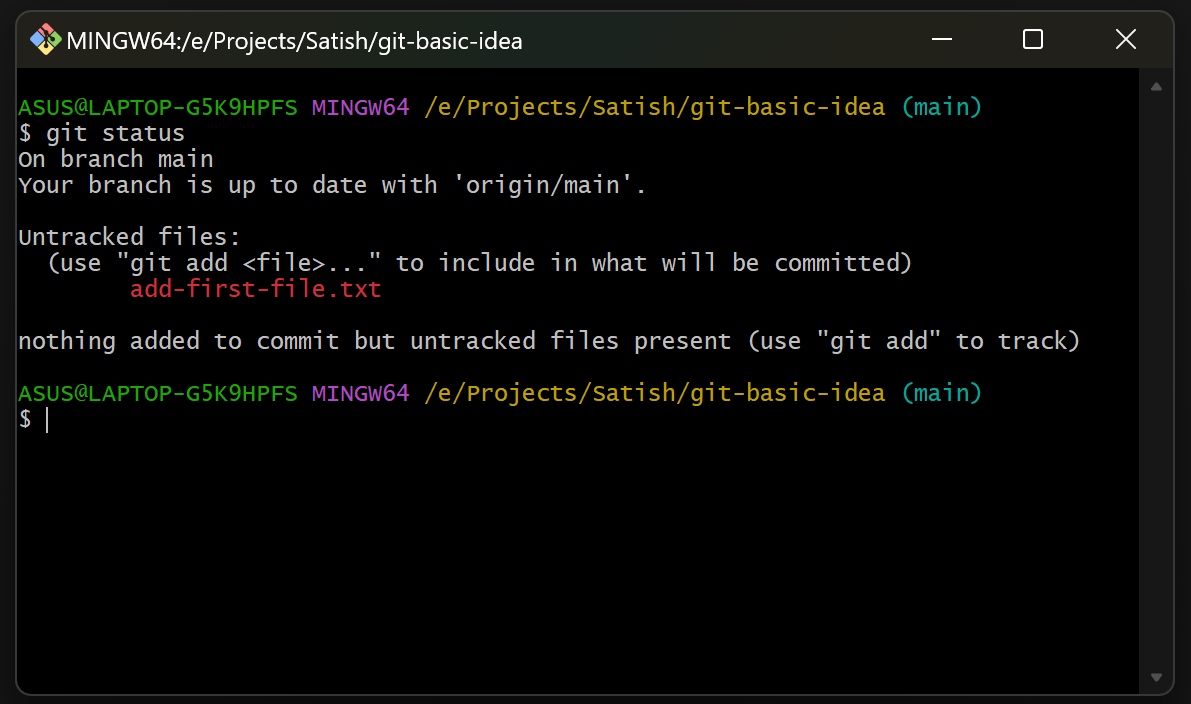
4. Check the Status of Your Repository
Use git status to see which files are tracked, untracked, or modified:
git status
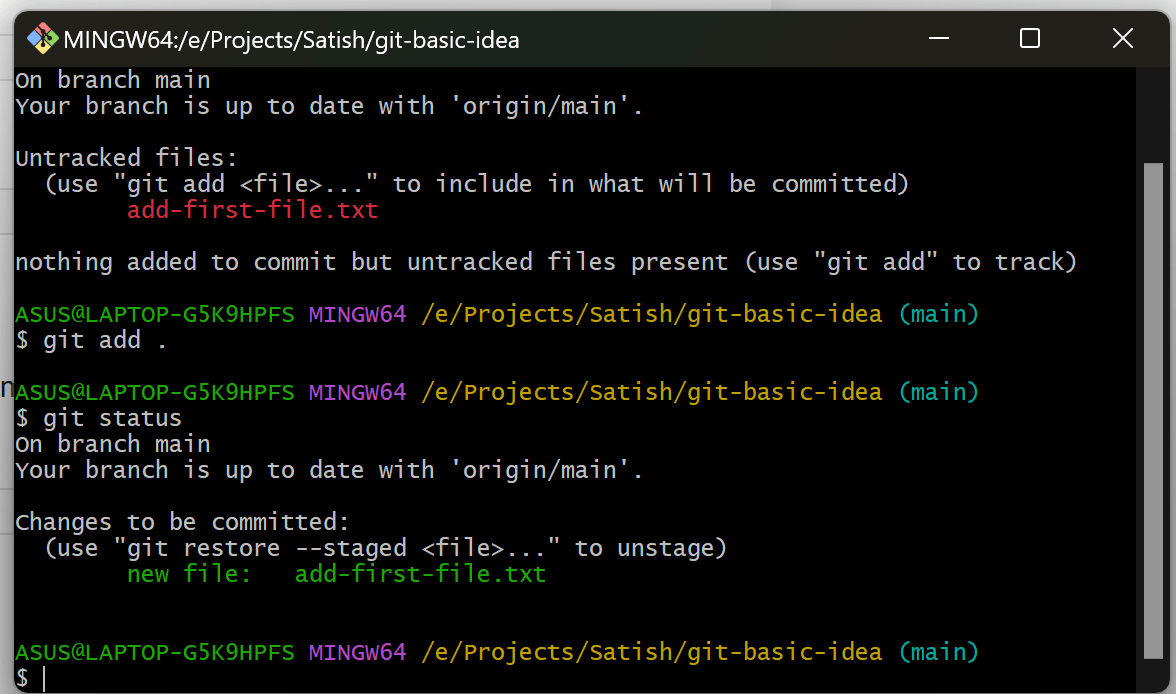
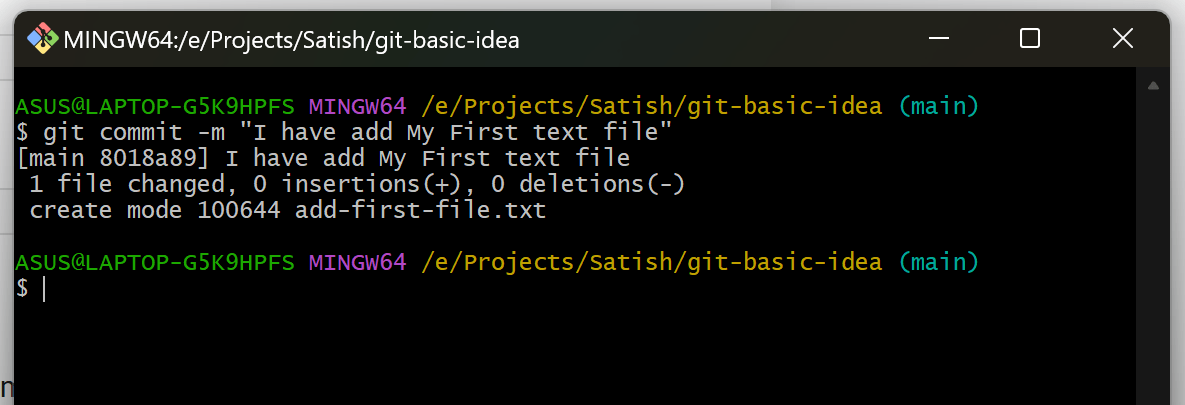
5. Commit Changes
Save changes with a clear commit message:
git commit -m "Your commit message"
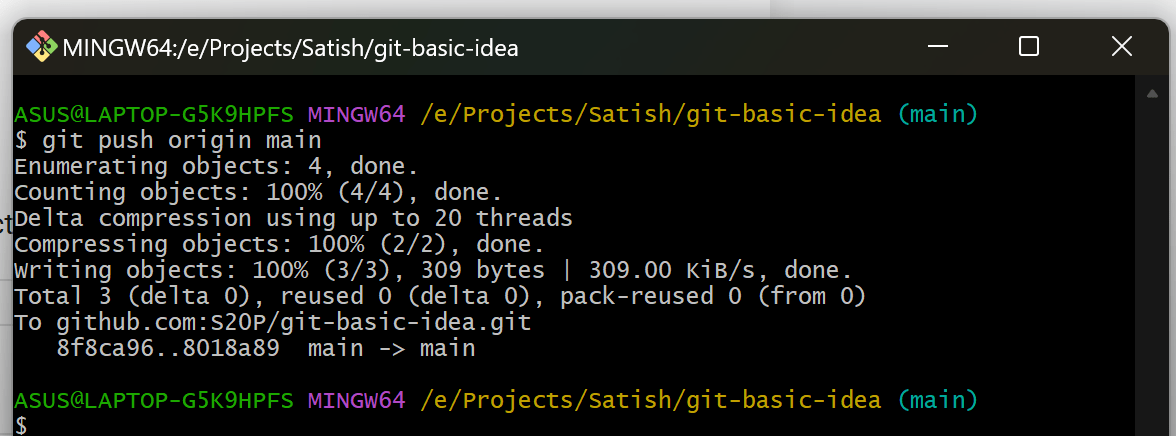
6. Push Changes to a Remote Repository
Upload your commits to a remote repository:
git push origin <branch-name>
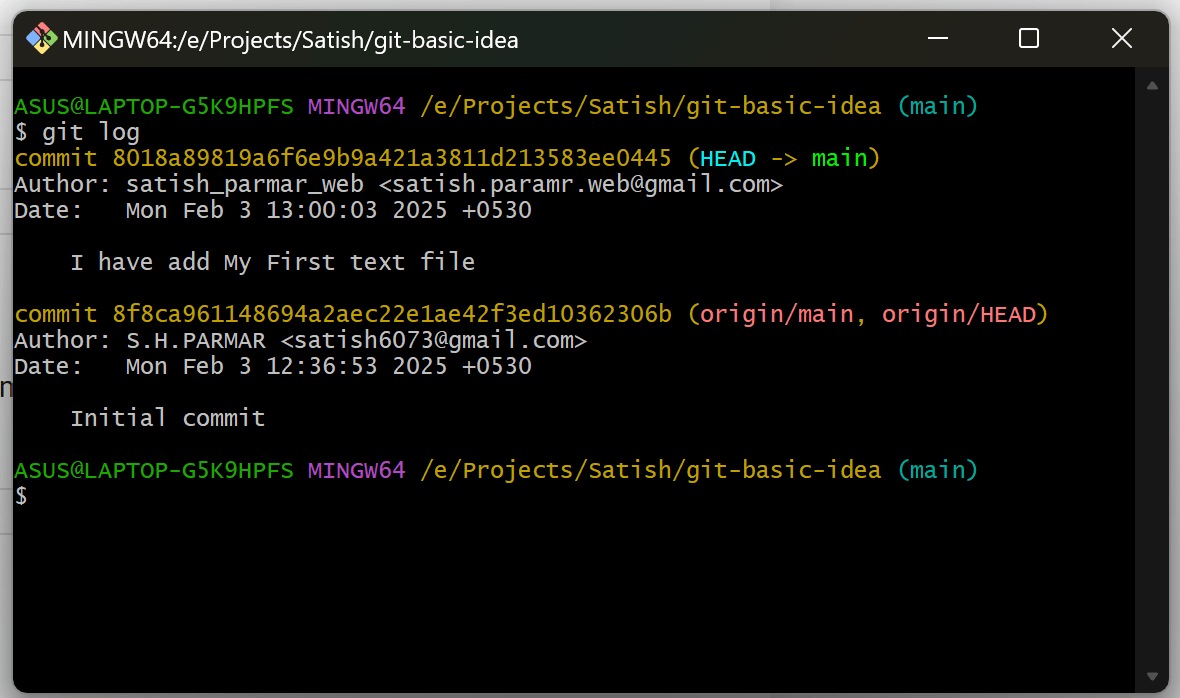
7. View Commit History
See a log of all commits with:
git log
This shows the commit hash, author, date, and commit message.
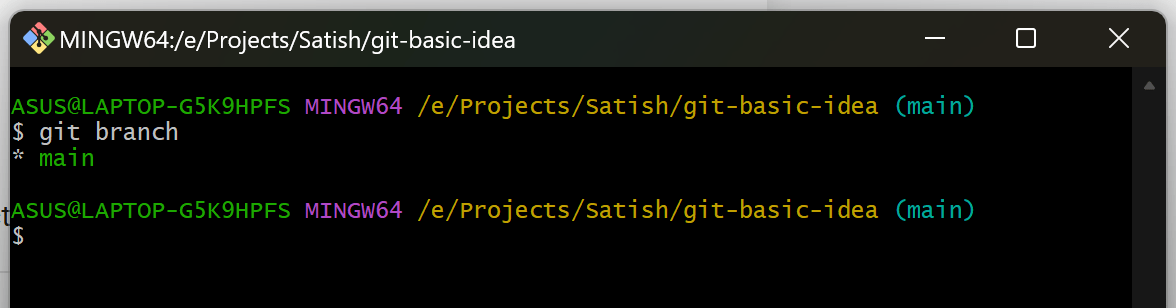
8. Create and Switch Branches
Branches allow you to work on new features without affecting the main codebase.
Check Current Branch
git branch
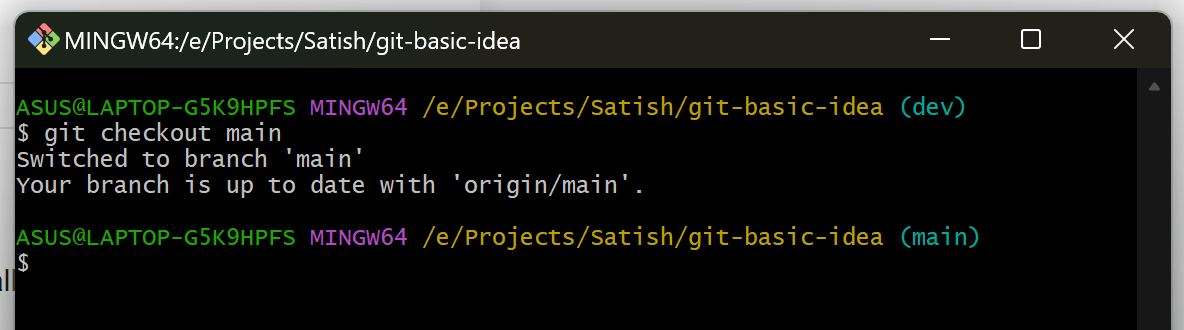
Switch to the new branch:
git checkout <branch-name>
Or create and switch in one command:
git checkout -b <branch-name>
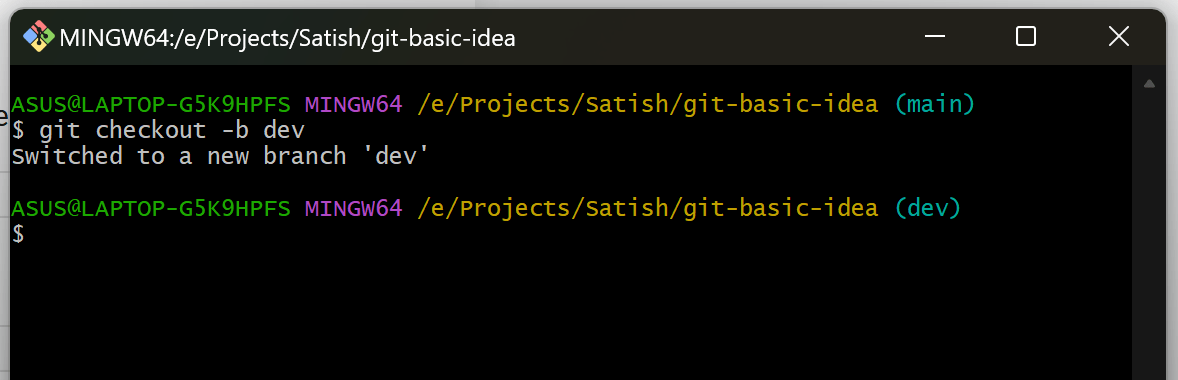
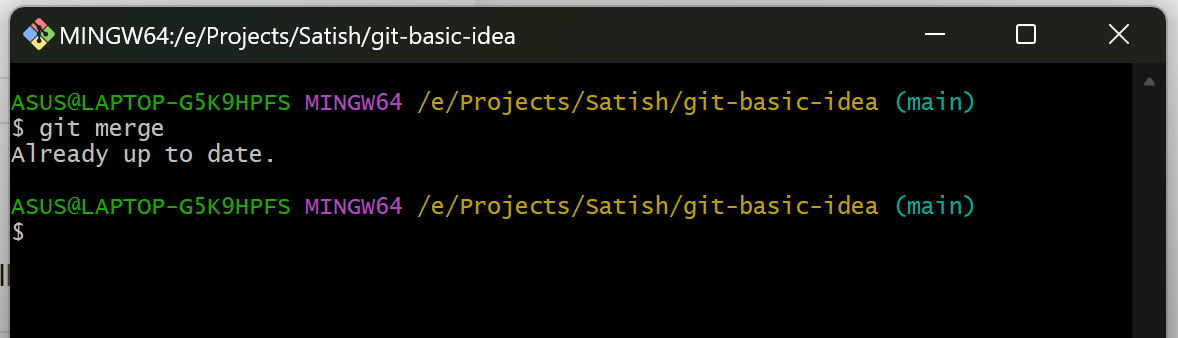
9. Merge Branches
Combine changes from another branch into the main branch:
git checkout main
git merge <branch-name>
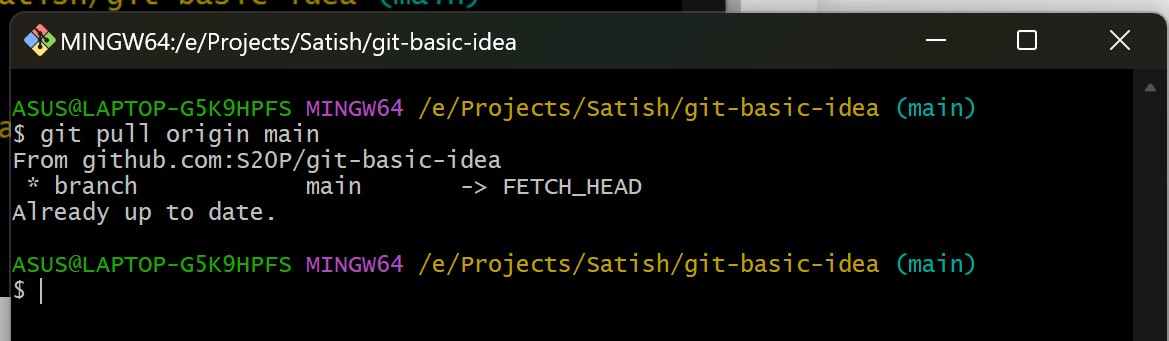
10. Pull Changes from a Remote Repository
To update your local repository with changes from the remote repository:
git pull origin <branch-name>
Pro Tips for Beginners
-
Write Clear Commit Messages:
Use descriptive messages like "Fix login button styling" instead of "Updated code."
-
Use .gitignore:
Create a .gitignore file to exclude files like node_modules or .env from being tracked.
-
Practice Regularly:
The more you use Git, the more comfortable you'll become.
-
Learn Git Branching Strategies:
Explore workflows like Git Flow or GitHub Flow for better collaboration.
Conclusion
Mastering Git is essential for every developer. By understanding these fundamental commands and best practices, you can efficiently manage your projects, collaborate with teams, and enhance your development workflow. Keep practicing and refining your Git skills to become a pro in version control!










0 Comments